Many people heard about Bitcoin and that isn’t surprising — it was a first cryptocurrency and till now it stays most popular and biggest. The Bitcoin success inspired many people and that’s why during last couple of years more than 1000 altcoins were created.
Without any doubt Bitcoin is the number one today. But do you know what’s the second cryptocurrency? Ethereum. When we speak about cryprocurrency ranking, we mean its Market Capitalization, in other words, the total price of all the coins (in dollars for example).

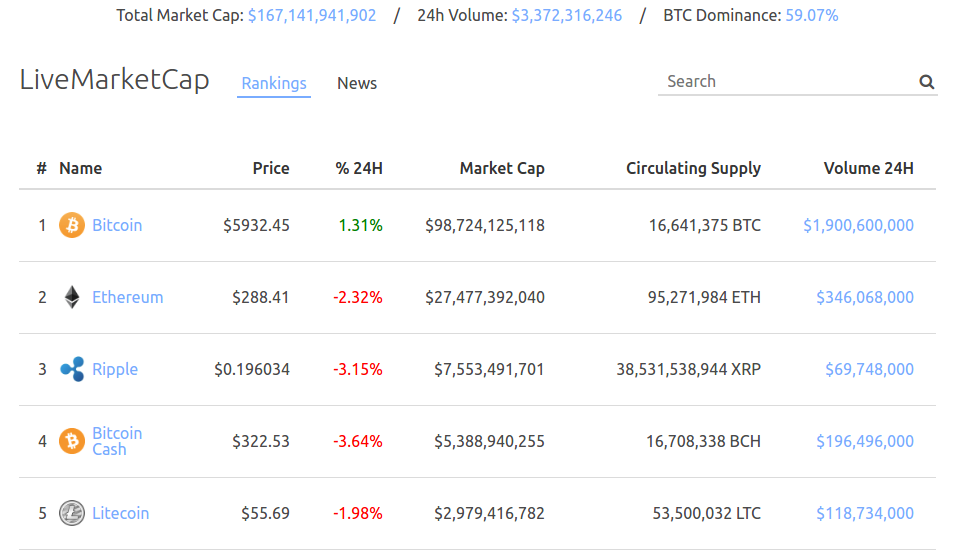
As you can see, Ethereum takes the lead over other altcoins by a huge margin and almost left behind Bitcoin in June 2017. In this article I’m going to explain the reasons why Ethereum is so popular and why the most of ICO use it.
As a data source for this article I decided to use LiveMarketCap.com. It provides a live ranking of all the active cryptocurrencies. You can read more about this platform and discover other great cryptocurrency services in my previous article.
The Idea Behind Ethereum
Ethereum launched recently, on 30 July 2015. One of its creators was Vitalik Buterin. He was born in Russia but moved to Canada at the age of 6. He was 19 when he proposed to community the ideas behind Ethereum.
Bitcoin is quite simple and easy to understand from the point of view of a normal user. There are wallets, anyone can send money from one wallet to another one or to many at once. The network is quite sophisticated and it allows to avoid any centralized server but it solves classic problems. Just a typical payment system: people, money, wallets, transactions and so on.
That’s clear. So what’s the Ethereum’s idea?
Now we can do one more step and create a new payment system which allows to anyone to create algorithms for wallets. Those algorithms can receive money, decide how much and to whom send money etc. With one important condition: the algorithms are transparent, predictable and no one can change it.
So, Ethereum developers added the possibility to create such algorithms. All the wallets in Ethereum divided into 2 types: operated by a human and operated by an algorithm.
Algorithms in Ethereum — they are called Smart Contracts — stored in the Blockchain. They are registered there forever and any participant of the network has its own copy because everyone has its own copy of the Blockchain. Thus, the result of an execution of a Smart Contract is identical for everyone.
As you can see, this invention extended the standard application of cryprocurrencies.
Smart Contract Examples
Which kind of algorithms we can write? For example, a financial pyramid. To do that, we can create a Smart Contract with following rules:
1. If we received an amount X from a wallet A, save this value in a debt table.
2. If after that we received an amount Y > 2*X, send 2*X to the wallet A, save this debt for the wallet B.
3. Etc for each participant.
4. An option: send 5% of each transaction to the author of the Smart Contract.
Another example? Ok, let’s create an auction:
1. If the auction is not finished, save participants wallet addresses amounts of bids
2. When the auction is finished, choose the maximum bid and send back all other bids.
There are plenty other applications: wallets with multiple owners, financial tools, bets, pools, lotteries, games, gambling etc.
Keep in mind the advantage: this is a Blockchain — it means everyone is sure there is no cheating, everyone can access to the algorithm code and ensure it works like expected. Smart Contract is not a human: if there is no bugs, it can’t go away with all the money, can’t go bankrupt etc.
Smart Contracts Limitations
With all those advantages, is there any limitations?
Actually, yes and here are few of them:
1. In a Smart Contract it’s hard to get a random values and other indeterminate behaviors. In some lotteries most advanced participants can “guess” the jackpot.
2. It’s not evident how to “hide” some information. For example, the list of participants and bids during an auction.
3. If a Smart Contract needs some information missing in the Blockchain (latest exchange rate of a currency for instance), some trusted source must provide it.
4. To use a Smart Contract, every participant must have Ether — a virtual internal currency. It means you can’t run a poll for participants who don’t have Ethereum wallets with Ether.
5. Smart Contracts are relatively slow. In the entire system only 3–5 transactions can be executed per second.
6. Usually Smart Contracts execute a very limited set of simple actions because every miner in the network must repeat those actions and verify the result.
7. If a Smart Contract has bugs, it’s forever. There is only one way to fix it: migrate to another Smart Contract. But it’s possible only if in the current Smart Contract there is a possibility to withdraw all the money and send to a new one. Most of beginner developers don’t think about this possibility.
In other words, like in any other domain, everything depends on a professionalism of a Smart Contract author.
Main Usage of Smart Contracts
Recently Ethereum found a new niche: ICO — Initial Coin Offering. On 1 January 2017 1 Ether costs about $8 and its peak it achieved in July 2017: $400 per 1 coin. The reason is lots of new ICOs. The willing to invest Ether in a project stimulates the demand and increases the price as a consequence.
Here are typical steps of a crypto startup:
1. You have an idea. Typically it’s related to cryptocurrencies and/or Blockchain.
2. You need money to develop and launch it.
3. You announce you accept Ether and give tokens using a Smart Contract.
4. You promote your project and raise the money you need.
How much a typical ICO can raise?
An average amount is around $10–20 millions and it’s often achieved in few days or even minutes. Normally, ICO is limited by time or total amount and it warms up the interest.
Sometimes the situation becomes comical. During one ICO, $35 millions were raised in 24 seconds. During another one, the participants were ready to pay a huge transaction fees of few thousand dollars per transaction to be placed higher in the queue. Huge demand and low channel capacity push people to increase transaction fees in order to participate on an ICO.
By September-October 2017 different ICO raised about $1.8 billions.
Still interested? Probably my recent article explaining some main rules and traps for beginners will be helpful. Remember, an ICO is an extremely high-risk investment. Please think twice before investing.
Thanks for reading! If you liked it , please support by clapping ������ and sharing the post. Feel free tp leave a comment below ��.
Dan Podolan is a blockchain developer and investor.
He is the CEO of LiveMarketCap.com. It provides live ranking of all the active cryptocurrencies and includes latest cryptocurrency news, market prices, charts and analysis.
Original article and pictures take cdn-images-1.medium.com site
Комментариев нет:
Отправить комментарий